Diagnostics
CT Scan
A computerized tomography (CT) scan, also known as a CT scan, is a diagnostic imaging technique that utilizes X-rays to produce detailed cross-sectional images, or "slices," of the body. These images show the bones, blood vessels, and soft tissues in greater detail than standard X-rays.
Ultrasonography
Ultrasonography is a medical imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound) to create images of internal organs and tissues.
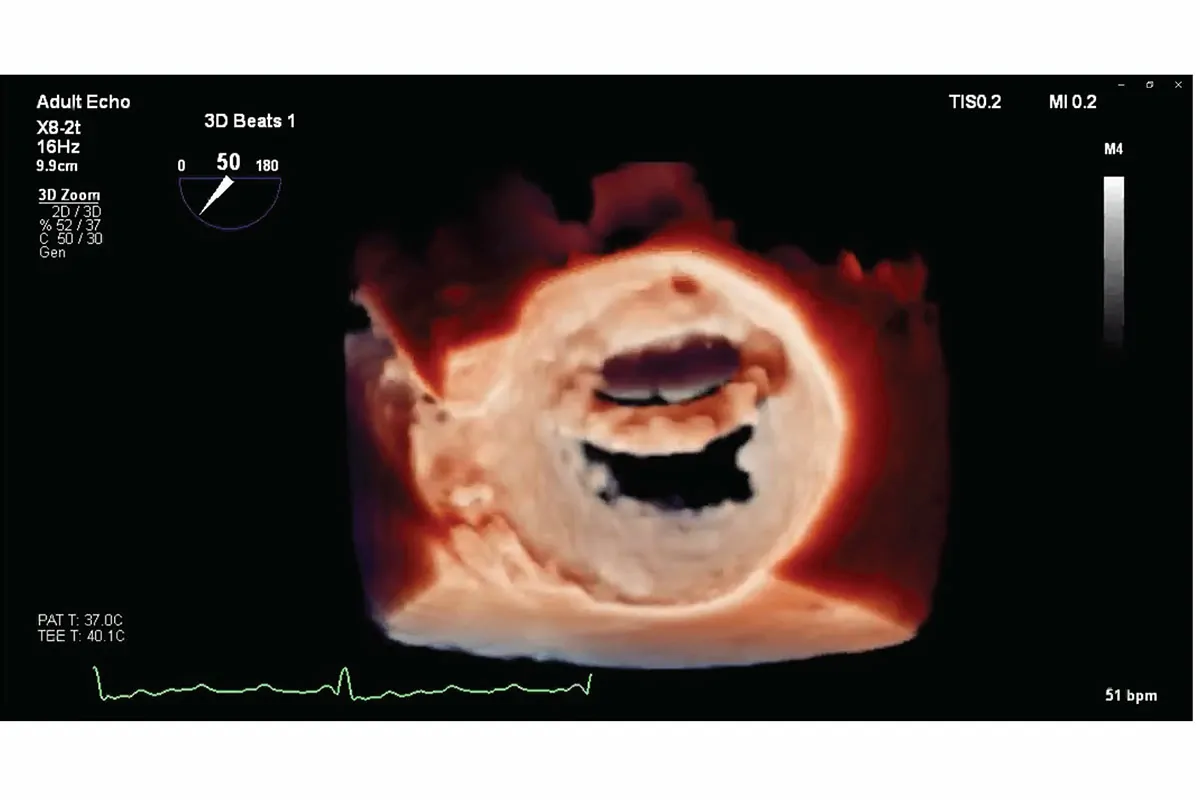
Echo 2D/3D
An echocardiogram is a non-invasive procedure used to evaluate the function and structure of the heart. During the test, a transducer (similar to a microphone) emits high-frequency sound waves that are too high-pitched to be heard. When the transducer is placed on specific areas of the chest, the sound waves travel through the skin and tissues to the heart. These waves then bounce off the heart's structures, or "echo," and are sent to a computer, which creates real-time images of the heart's walls and valves.
Sonomammogram
A sonomammogram, also known as a breast ultrasound, is often used alongside mammography for breast imaging. This technique utilizes sound waves to create images of the breast tissue, allowing doctors to closely examine lumps, cysts, and other abnormalities. It is particularly effective in distinguishing between solid masses, which may be tumors, and fluid-filled cysts.
Orthopantomogram
The Orthopantomogram (OPG), also known as a panoramic radiograph, is a dental X-ray that captures a complete view of your mouth, teeth, and jaw in a single image. This includes both the upper and lower jaws, the temporomandibular joints (TMJ), and all teeth. It is a crucial diagnostic tool used by dentists and oral surgeons for a variety of purposes.
X-Ray
X-rays are a vital diagnostic tool used by medical professionals to assess and diagnose a wide variety of medical conditions. These scans produce detailed images of the body's internal structures, including bones, organs, and tissues, aiding in the identification of numerous health issues.